Everything you need to know about materials in Unity: from simple to complex effects
07 Sep 2025

Materials in Unity are one of the most important aspects of rendering that help create realistic or stylized surfaces for objects in 3D space. They determine how an object will interact with lighting, reflect or absorb light, and what textures will be used to create various visual effects. In this article, we will take a detailed look at materials in Unity, their properties, types, and how to configure them to achieve optimal visual results.
What is a Material in Unity?
A material in Unity is a component that is applied to objects, defining their visual properties. Materials include information about color, texture, reflection, transparency, lighting, and many other characteristics that affect how an object's surface appears in the game. Materials are associated with shaders, which are programs that calculate how exactly these properties will be displayed on the screen.
Materials in Unity usually consist of several basic components:
A shader is a program that describes how an object should be displayed depending on the conditions of the scene (for example, lighting).
Textures are images that are applied to an object to enhance its appearance, such as to simulate complex surfaces like leather, stone, or metal.
Material Properties are settings that allow you to customize visual effects like gloss, transparency, and lighting.
Basic Material Properties in Unity
Unity provides several material properties that can be customized to achieve different visual effects.
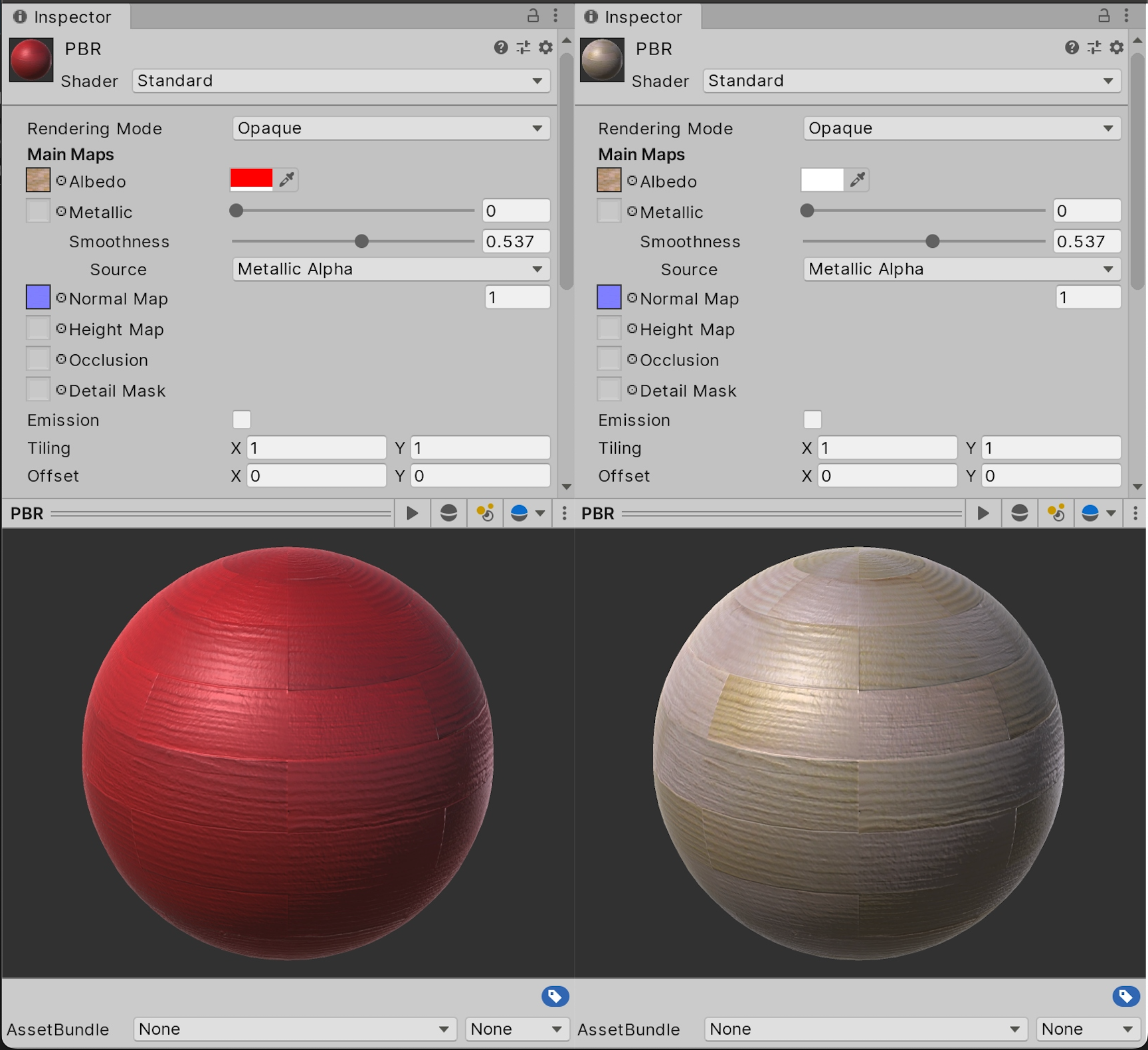
Here are the main ones:
Albedo (Primary Color)
This is the primary color of the material or texture that determines how the surface of the object looks. In older versions of Unity, this property was called "Diffuse". It determines how the object will reflect light, and what will be visible in its color. Albedo is commonly used for texturing surfaces.
Metallic
This setting controls how much the object will look like metal. The higher the value, the more metallic the surface will be. If a material has a high metallicity value, its reflections will be brighter and clearer, resembling a metal surface. For non-metallic objects, this value should be set to 0.
Smoothness
A parameter that affects how smooth the surface will be. A high value makes the surface more reflective, while a low value makes the surface more matte. This property is important for creating various materials such as glass, plastic, or wood, which can be either glossy or matte.
Normal Map
A normal map is used to create the illusion of detail on a surface without having to add additional polygons. This allows you to add effects such as scratches, folds, or surface textures. A normal map determines how light will interact with the surface, creating the illusion of details that do not actually exist.
Bump Map
A bump map works similarly to a normal map, but is less precise in its effect. Unlike a normal map, it does not change the direction of the normals, but only "bends" the light according to the map. Bump maps are often used to create less complex effects than normal maps.
Occlusion Map
This setting is used to simulate effects related to global illumination, such as darkening the recesses of an object. This allows for more precise control over how light falls on objects, especially in places where it might be "blocked" by other surfaces.
Emission
Emission makes an object appear to be a light source. This setting adds a glow effect that makes an object appear bright, even in a dark scene. This is useful for creating glowing objects, such as lamps or neon elements.
Transparency
The transparency of a material controls its ability to transmit light, allowing for effects such as glass, water, or other translucent surfaces. Transparency is controlled using an alpha channel in the texture, which determines how transparent the object will be.
Specular
Specular factor controls how much the object reflects light. Unlike metallic materials, where the reflection depends on the color of the material, specular materials use this parameter to adjust the reflections on the surface.
Detail Maps
In Unity, you can add several additional textures that affect the appearance of an object, such as fine detail textures. These maps add additional layers of visual information, such as fine dirt or marks on the surface.
Using Shaders with Materials
Shaders are the core of materials in Unity. They are programs that are responsible for rendering objects. Using shaders, you can control in detail how the surface of an object will be displayed, control lighting, reflections, transparency, and many other visual effects.
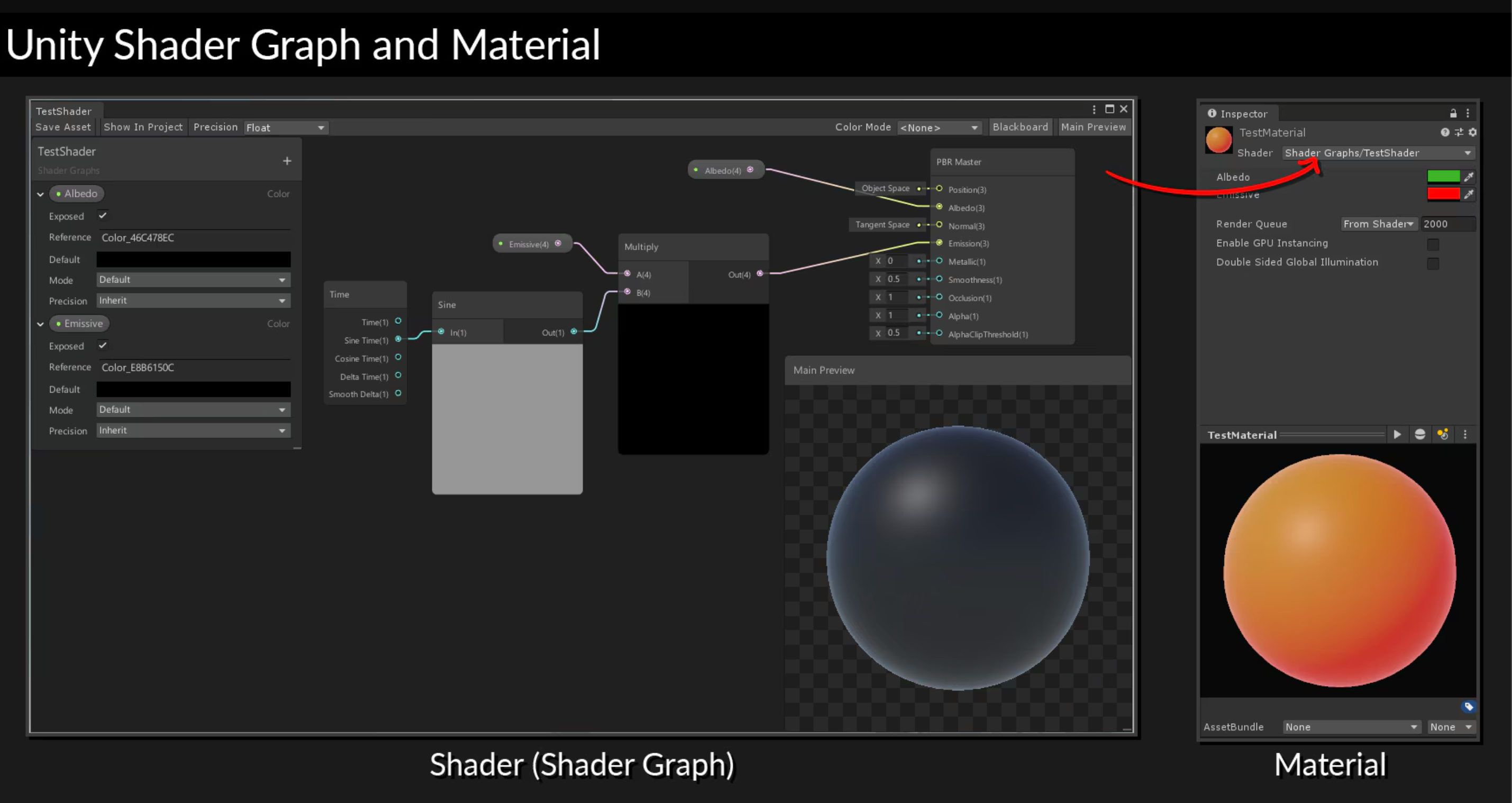
Standard Shader
Unity uses the Standard Shader by default, which supports all of the above options and allows you to create materials with a wide range of visual effects. This shader is great for most tasks and is quite versatile.
Surface Shaders
Surface Shaders allow you to create more complex materials with lighting, including interaction with light sources and shadows. This type of shader abstracts many of the details and automatically handles interaction with various light sources in the scene.
Unlit Shaders
Unlit Shaders are shaders that do not depend on the lighting in the scene, creating effects such as for screens or objects that should not be shaded. These shaders are useful for creating post-processing or UI effects.
Shader Graph
Shader Graph is a tool in Unity that allows you to create shaders using a visual interface. In Shader Graph, you can combine different nodes to create complex materials and effects without having to write code. This is especially useful for artists and designers who want to work with shaders without having any programming experience.
Optimizing Materials
Properly optimizing materials is important to ensure good game performance. There are several factors to consider that can affect rendering efficiency:
Using Texture Atlases
Texture atlases allow you to combine multiple textures into one. This reduces the number of requests to the graphics card and improves performance.
Minimizing the Number of Materials
Each material requires computation on the GPU. The more materials in a scene, the more resources are required for rendering. Using one material for several objects, where possible, will help improve performance.
Using Standard Shaders
Standard shaders, such as the Standard Shader, are optimized for most use cases and are generally faster than hand-written shaders. Unless you need complex effects, it is better to use standard shaders.
Reducing Texture Resolution
Using high-resolution textures can have a significant impact on performance, especially on mobile devices. For objects that are far away or do not require high detail, it is worth using lower-resolution textures.
Conclusion
Materials in Unity are the basis for rendering objects and affect how they will look in your game. From color adjustments to the use of complex textures and shaders, materials allow you to achieve a variety of visual effects, from simple objects to realistic or fantasy scenes. It is important to understand how to properly configure materials to ensure the desired visual style and performance. Using standard shaders, texture atlases, and proper optimization will help you create a beautiful and performant game.
Related games
Jungle Cars Trip Multiplayer - Invite your friends!
Game: Perform tasks and rest cool. 2201 people play!
Play gameElectron in the transistor-resistor kingdom
Game: Perform tasks and rest cool. 2624 people play!
Play gameRelated news
Complete Particle System Guide: Creating Fire, Smoke, and Ma...
Unity Particle System is a powerful tool for creating visual effects in real time. Particles are used in everything from...
Read moreRendering in Unity: Pipeline Overview and Creating Realistic...
Explore Unity's rendering pipelines and learn how to create stunning, realistic water effects. A complete guide for developers seeking performance, flexibility, and visual impact.
Read moreCreating Realistic Landscapes in Unity with Terrain
Learn how to create stunning and realistic landscapes in Unity using the Terrain system. Tips, tools, and techniques for building immersive game worlds.
Read more




